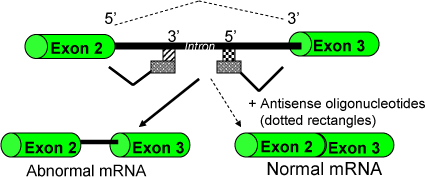
Figure 8-1. Gene Therapy for Tazswana. Alternative splice patterns are shown. Wild-type splicing (dashed line and arrow) results in exon 2 juxtaposed to exon 3. The alternative splice pattern (solid lines and arrow) results in retention of a portion of the intron between exons 2 and 3. Oligonucleotides (10 nt long) can affect alternative splicing of the β-globin pre-mRNA. The β-globin pre-mRNA (top of figure) that causes Tazswana’s β-thalassemia is depicted. The mutation causing the aberrant 5′ splicing sequence is represented by a checkered-box. The cryptic 3′ splicing sequence in the intron is represented by a striped box. The antisense oligonucleotides are represented by polka dot, grey rectangles.
Figure modified from “Therapeutic potential of antisense oligonucleotides as modulators of alternative splicing” Sazani, P. and R. Kole. (2003) The Journal of Clinical Investigation 112(4)481–486.
